The 2019 global pandemic has opened the door to a permanent shift in consumer behavior, accelerating ecommerce by half a decade and boosting online services across a variety of industries.
For years, technology and mobile connectivity have empowered shoppers, moving from single physical store channels to omnichannel commerce. Consumers have more choices than ever when it comes to purchasing options. Pricing; convenience; personalization; last mile delivery; ease of payment; and selection are just a few amongst the differentiating factors that contribute to online purchase decisions today.
However, the economic crisis in 2022 and the inflationary pressure, has put a strain on profitability and cost management for companies across the globe. Rising energy costs have led to manufacturing constraints and reduced volume quotas. Inflation has led to greater price and deal-seeking shopping behaviors with more attractiveness for private labels. Supply Chain and logistics rising costs have driven warehousing capacity constraints and a reduction in cross-border sales. Finally, shoppers have become more conscious about their purchasing patterns, preferring sustainable choices, eco brands, ethical companies and data sharing transparency.
Since Facebook’s rebranding into Meta in 2021, a lot of attention has been drawn on the Metaverse and how Web 3, our next iteration of the internet, would enable real-time, interconnected, immersive experiences. Web 3 is powered by innovations in the fields of Artificial Intelligence (AI); Extended Reality (XR); Blockchain & Cryptocurrencies; Digital Wallets; and Mobile hyperconnectivity.
Despite the tech hype around the Metaverse, expected acceleration in the space hasn’t seemed to deliver expectations as quickly as anticipated by the media. Meta was one of the first large tech companies to kick off mass layoffs across the globe, together with Amazon, and Google.
Restructuring as a possible consequence from the pandemic and the current economic crisis, tech companies appear to shift their priorities and capability investments towards specific pockets of research and innovation.
As a result, 2022 and 2023 have brought exciting acceleration in disruptive tech innovations that will revolutionize our daily lives, specifically in Artificial Intelligence (AI), marking a New Era. In 2022 AI became THE tech to watch ahead of the Metaverse, positioning itself as the ‘2023 Tech of the Year’.
2023 and beyond will require brands and retailers to boost creativity and embrace new partnerships to engage with consumers and shoppers, in light of new trends and technology.
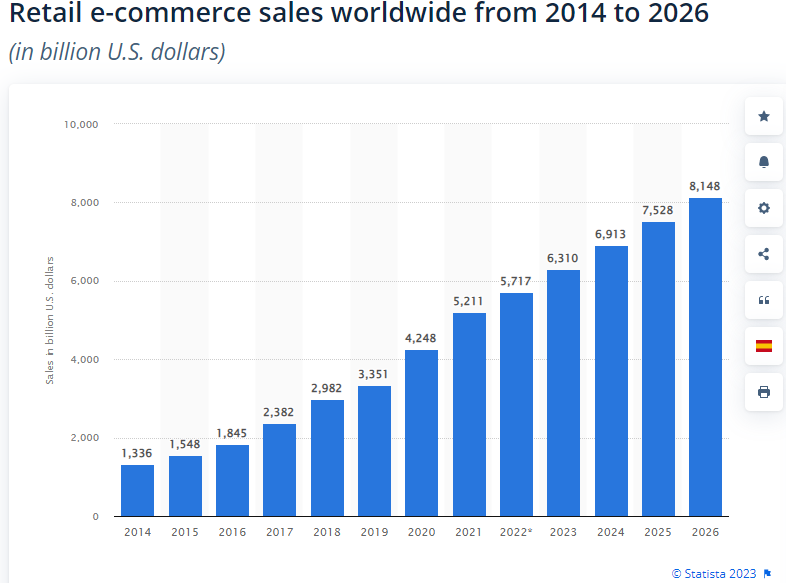
In this context, ecommerce will continue to provide exceptional potential with expected revenues of $6.3T in 2023 and a predicted 11.5% CAGR to 2027. The share of ecommerce to total retail globally will continue to grow with a predicted 21% share in 2023 and a 24% share by 2026.
New opportunities to deliver ever-more engaging, delighting, connected shopping experiences in an omnichannel commerce world will push brands and retailers to adopt innovation and new strategic revenue management solutions facilitated by tech.
Hyper-personalization and virtual immersion powered by AI and XR; seamless and traceable payments powered by blockchain and cryptocurrencies; supply chain management and logistics’ costs optimization powered by AI, will allow brands to build unique connections with their consumers, meeting them across every digital touch point.
Significant opportunities exist for businesses who are willing to embrace change, to innovate, adapt, and respond. As brick & mortar retailers adopt an omnichannel approach and look to build new online stores, the difficulty to remain competitive in the space intensifies. Innovative companies looking to win online must therefore understand key Commerce trends and leverage technology innovation to stay on top of their game.
In this post, I consolidate some of the trends and innovations that I find most interesting and relevant to achieve success online in 2023 and beyond:
- Technology Innovation:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Augmented and Virtual Reality
- Metaverse
- Big Data & Data Science
- Supply Chain and Last Mile Delivery
- Social & Live Commerce
- Retail Digital Media Networks
- Omnichannel Approach
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is at the forefront of innovation in ecommerce. Since the announcements of ChatGPT last November, and GPT-4 most recently, articles have been published daily on the opportunities available thanks to AI applications.
Through its majority stake investment into OpenAI, Microsoft is now leading the way in Natural Language Generation and Processing (NLG, NLP), but several applications of AI are currently disrupting industries and businesses across the globe. From machine learning (ML), to natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLM), to robotics, applications appear to be virtually endless.
Tech giants are all competing in the AI race: Microsoft with the integration of ChatGPT within Bing; Google with the recent release of Bard; AliBaba with their own LLM Tongyi Qianwen; IBM with their Watson natural language understanding service; Amazon with their virtual assistant Alexa, with AWS, and with their NLP system Comprehend.
Meta appears to have fallen behind with recent leaks of their LLaMA language model, but they promise their own version of ChatGPT by year-end and recently released their AI-powered animation tool.
The impact of generative AI on the global ecommerce sector is already valued at $5.9T and according to Gartner, the number of businesses adopting artificial intelligence grew by 270% in the last four years.
Ecommerce companies are amongst the leading adopters of artificial intelligence, followed by FinTech and Online Media.
According to recent studies by Gartner and PwC, the use of AI to accelerate ecommerce will continue to increase in the next five years:
- 84% of eCommerce businesses are either actively working AI solutions into their business or have it as a top priority.
- 86% of decision-makers state that in 2022, artificial intelligence is a 'mainstream technology'.
- The use of voice recognition is important as 22% of users prefer talking to an AI voice assistant instead of typing.
- Another 26% of respondents state that AI voice assistants give them an easier way to use other features.
- In a 2021 survey, global consulting firm PwC reported that more than half (52%) of business decision-makers have found that the integration of AI tools in their practices has boosted productivity.
- 75% of IT leaders stated that usage of AI technology will help enhance security.
- 23% of companies interviewed have already implemented AI chatbots and another 31% of companies plan to deploy AI chatbots in the future.
- The global Conversational AI market size is expected to grow to $13.9 billion by 2025.
- Facebook Messenger hosts over 300,000 active chatbots. Chatbots are also one of the most popular methods of implementing AI in eCommerce.
- Gartner predicts that by the end of this year, artificial intelligence will handle 15% of all customer service interactions globally.
In summary, looking at ecommerce globally, major opportunities exist to streamline, optimize and improve online businesses through the use of AI technologies with major applications in the following areas:
- Online personalization: leveraging Big Data and ML to deliver optimized ,personalized, fun and engaging online shopping experiences.
- Customer Support: leveraging NLP and LLM to automate online customer support services through bots and virtual agents, allowing humans to deliver more valuable contributions.
- Digital Marketing: leveraging ML to optimize online campaigns; customer segmentation and targeting; improve ROI.
- Logistics: from ML to robotics numerous opportunities exist to optimize warehouse management and logistics, reducing waste and excessive stock.
- Supply Chain: leveraging ML to improve inventory flows, optimizing delivery routes and stock holdings across supplier and manufacturers’ networks.
- Product Development: leveraging Big Data and ML to identify new trends and opportunities for new product developments, but also leveraging IPA systems to create new products intelligently with the help of virtual agents.
Unsurprisingly, the Fashion industry has been prolific in adopting these new systems and we see popular fashion brands like Zara, H&M, Dior, Macy’s, and Nike already using AI in their business models. Whether through AI chatbots, personalisation, or trend forecasting, AI is already helping both small and big fashion companies promote goods, improve sales, and enhance the customer experience.
Important applications already align with sustainability trends and the need to reduce fabric and clothing waste. Predictive analytics, powered by AI, heavily supports buying and merchandising teams in the apparel industry to make better decisions and estimations about future trends and purchased volumes.
Thanks to advances in generative AI, businesses will be able to create virtual images of garments’ designs and accessories based on customer demands and fashion trends. These images will then be shared with consumers through social media channels, and ecommerce platforms to generate feedback loops and inform clothing manufacturing.
ASOS already tested this AI use case holding virtual photoshoots with virtual images of clothing on real-life models, providing shoppers with hyper realistic representations of the garments to finally gauge their interests.
Large online marketplaces and peer-to-peer platforms are also benefiting from AI technologies to offer tailored, personalized experiences and drive retention and conversion. Amazon and Alibaba, for example, are at the forefront of the use of AI technologies to manage their platforms. These two giants have already been using AI for years to drive product recommendations; to facilitate the shopping experience through the use of Voice search through virtual assistants like Alexa; to manage their supply chain to optimize deliveries, inventory flows, logistics.
Large language models (LLM) powering generative AI have been at the forefront of the AI revolution this year and will revolutionize how online experiences are delivered and generated for consumers across the globe.
With systems like ‘generative adversarial networks’ (GAN) that will help generate new content online, product information management platforms (PIM) are now incorporating these services as part of their standard offering. Salsify, one of the largest product information management platforms, already announced their own generative AI product offering. It becomes harder and harder to distinguish between AI-generated online product campaigns and real ones, but the implications for brands will be striking.
Online production functions within ecommerce companies will be able to streamline, automate, and instantly syndicate online content to fully optimize online product detail pages, possibly personalizing experiences even more by focusing on features most relevant to specific shoppers’ clusters.
Creativity will be fully nurtured, as virtually no limits will exist in creating rich content to make experiences more engaging and captivating.
AR / VR
The boundary between the virtual and real world has become blurrier, with new virtual breathtaking experiences finding their way in our daily lives. Virtual Reality (VR) has been talked about for many years, but thanks to technological advancement, it has finally found its place in generating realistic images, sounds, and sensorial-like experiences. Augmented Reality (AR), which adds virtual components to the real world, has also followed through and both AR / VR will remain big technologies of the future.
Augmented and Virtual Reality have experienced a push since the global pandemic, as logistics costs have become more significant for online retailers. Offering free delivery and returns is not a luxury that many companies can still afford, especially as they look to create more sustainable and environmentally-friendly operating models.
This is where augmented and virtual reality technologies can offer a strong advantage, allowing consumers to ‘virtually’ try on their favorite products or to interact with them in a virtual store before completing a purchase.
As these technologies find prominence thanks to an increasingly available range of headsets and virtual reality platforms, ‘virtual immersive shopping’ becomes an ecommerce reality, building the foundation of Web 3.0.
In ecommerce, we already see major applications for these technologies in the following areas:
- Social Media apps and camera filters: 75% of the global population and almost all smartphone users will be frequent AR users according to Deloitte, and the majority are discovering AR through social media apps. Snapchat and Instagram have been pioneers in developing AR filters and fashion companies in adopting them as with the 2021 Dior campaign on Snapchat.
- Virtual Try-On: Research from Modern Retail suggests product demonstration via virtual try-on and real-world overlay has seen the biggest increase in AR usage between 2017 and 2022. Research by Shopify shows that AR can improve conversions by 97% and slash returns by up to 40%.
Companies in the beauty industry have been leading the way in trialing these new products, from L’Oreal, to Sephora, to Clarins. Fashion companies have also caught up with Farfetch ‘try on sneakers’, Marc Jacobs and Prada using Snapchat’s try on tool for bags.
- Virtual Showroom: this is the AR technology that allows customers to virtually place items in the environment around them and the main difference between virtual try-on and showroom is the customer flipping the camera around. Research from Shopify for example, found merchants who add 3D content to their stores see a 94% conversion lift, on average.
- Gamification: AR mirrors in physical stores, AR gamification in-store. China currently leads the way in smart mirror usage, but there is a strong appetite for this technology in other markets too. Snapchat research shows that 21% of consumers would go out of their way to visit a store with a smart mirror and 33% would use it in stores they already regularly visit.
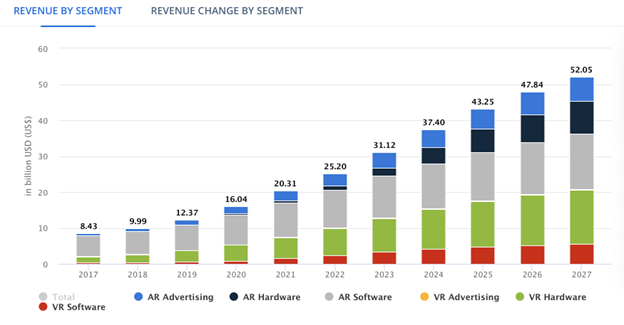
Global revenue in the AR & VR market is projected to reach US$31.12bn in 2023 with an annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2027) of 13.72%, resulting in a projected market volume of US$52.05bn by 2027. The market's largest segment is AR Software with a market volume of US$11.58bn in 2023.
Statista, 2023
ASOS re-introduced augmented reality for ‘virtual fitting’ functionalities to reassure consumers still reluctant to try and return clothes purchased on its site.
Engaging, personalised experiences will become more prominent, embedding the commercial and transactional component within highly experiential brand propositions that will create value for consumers. As a consequence, rising technologies like AI, AR and Voice will also see an accelerated and wider growth across multiple industries to address new needs of ‘convenience’ demanded by a larger online consumer base.
These estimations give marketers and platforms enough reasons to test and invest in these technologies.
Large tech companies like Meta and Google are trying to accelerate this trend by investing in AR and VR tools. Google recently acquired Raxium, a startup that specializes in smart glasses with new technologies that could significantly improve Google’s previous attempt at Google Glass.
Meta announced Meta Reality in October 2022 and Infinite Display (their custom-built optical stack), confirming they will continue improving their future generations of VR headsets.
Metaverse
Defining the Metaverse is still a challenge, with multiple technological innovations being mistakenly used interchangeably for a metaverse definition (VR, Web 3). However, the potential for the Metaverse to disrupt the digital industry and become an integral experience of Web 3, the next phase of our interoperable, hyper-connected internet is clear. As with previous shifts in technology, from Web 1.0, to Web 2.0 driven by mobile connectivity, to cloud infrastructures, new technological innovations can quickly settle in our daily lives. The Metaverse has the potential to impact the customer experience, omnichannel sales, marketing, product innovation, and community building.
When looking at the tech industry and the major investments in AI; XR; blockchain technologies; digital ledgers, it is evident that the next wave of the internet, Web 3, is already here.
These technologies will all enable the Metaverse, and fantasizing about a world like we’ve seen in ‘Ready Player One’ is unavoidable.
Despite Facebook rebranding into Meta in 2021 and Mark Zuckerberg’s reference to the Metaverse as ‘ … the successor to the mobile internet…” where “We’ll be able to feel present—like we’re right there with people no matter how far apart we actually are.”, providing a definition for the Metaverse remains challenging.
Yet I found Matthew Ball’s Metaverse primer inspiring:
…“The Metaverse is a massively scaled and interoperable network of real-time rendered 3D virtual worlds and environments which can be experienced synchronously and persistently by an effectively unlimited number of users with an individual sense of presence, and with continuity of data, such as identity, history, entitlements, objects, communications, and payments.”...
This is where the connection between what the Metaverse will enable and the hyper-connectivity offered by Web 3 is apparent.
The Metaverse will have three main features that are agreed upon at its most basic:
- A sense of immersion
- Real-time interactivity
- User Agency
And in a broader sense it will also include:
- Interoperability across platforms and devices
- Concurrency with thousands of people interacting simultaneously
- Use cases spanning human activity beyond gaming
Understanding the potential of the Metaverse and its effects should be part of strategic discussions amongst industry leaders looking to understand how virtual environments will co-exist with physical ones in the future. Building safe virtual environments in a responsible manner for consumers and in line with the vision of the next iteration of the internet are some of the open reflections that need to be tackled.
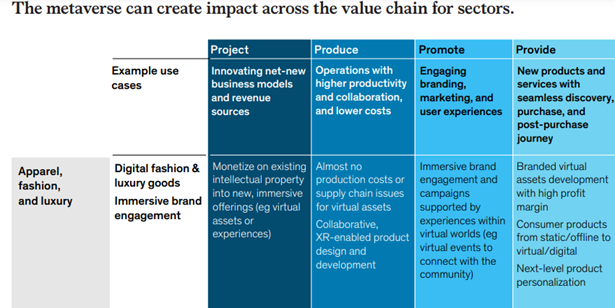
According to McKinsey, value creation in the Metaverse is already estimated at $5 trillion by 2030. Additionally, it is estimated it may have a market impact of between $2 trillion and $2.6 trillion on ecommerce by 2030, depending on whether a base or upside case is realized.
Of all the potential drivers of the economic impact of the Metaverse, ecommerce will be the largest.
From a commerce standpoint, innovators are already prolific in the space with Sotheby’s owned marketplace for NFTs; virtual-only fashion company Fabricant; startups promoting immersive retail experiences like Obsess and AnamXR.
In Apparel & Fashion, consumers already spend much of their time using digital screens for product research, online shopping, and brand interactions. This is promising for the Metaverse to become a meaningful avenue for consumers looking to buy and wear fashion.
Decentraland’s Fashion Week events have received major industry attention with participation from major luxury and fashion brands like Dolce & Gabbana, Estée Lauder, and Etro. These experiences are blockchain-based with fashion sold and worn as NFTs. Luxury is often about being part of a community, enhancing one’s identity and this same potential exists virtually in the Metaverse.
As Gucci’s executive vice president and chief marketing officer Robert Triefus said in McKinsey’s latest State of Fashion report. “The idea that everything has to be physical is very quickly being disproved.”
Virtual clothing is already being embraced by a multitude of brands, willing to satisfy consumers’ appetite for creativity, status, and exclusivity in creating their first digital identities. The gaming skins market already reached $40 billion in 2020, and the metaverse could become THE next growth opportunities for fashion and luxury after ecommerce.
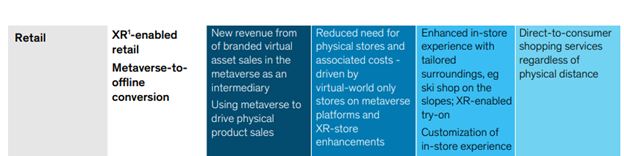
In retail, traditional brick-and-mortar retailers have already felt the need to quickly adapt to technological change to survive in an omnichannel environment.
The Metaverse provides opportunities to strengthen retailers’ competitive advantage by offering unique experiences, and fostering brand communities. Virtually and digitally enhancing retail is not a new concept, but it may be needed more and more for players to win.
It is estimated that 25% of consumers have shopped in virtual stores with 70 % of them having made a purchase. Brands can leverage VR / AR to offer a new level of experience: 3D navigable showrooms and store shelves’ spaces to facilitate virtual try-on and purchasing of virtual or physical goods.
Several brands have already tested the potential with Dyson’s VR-enabled digital store and furniture companies like Crate & Barrel, Wayfair, and WestElm partnering with Pinterest to leverage AR to test furniture fit in real spaces. Brands now have the opportunity to create globally accessible stores in virtual spaces, reducing the need for physical footprints. Samsung has tested this concept with a recent store on Decentraland where consumers can earn NFTs. Additionally, retailers like Ralph Lauren, Urban Outfitters, and Walmart already filed trademarks related to opening virtual worlds.
Virtual parcels of land are recurrently being sold with the intent to build shopping malls and on top of commerce opportunities, brands in the food, sporting, entertainment industry are leveraging virtual spaces for advertising, brand activation, and recruiting purposes. Chipotle for example opened a virtual restaurant to support their Halloween campaigns in 2021 with free giveaways to redeem at their physical restaurants.
Opportunities for retailers in the Metaverse are already apparent and being tested across a variety of industries.
We can safely assume they will continue to grow and provide a strong competitive advantage for companies willing to stay relevant and willing to build strong connections with their consumers.
Big Data & Data Science
Big Data combines structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data collected by companies that can be mined, organized and analyzed to be used in machine learning projects, predictive modeling, and other advanced analytics applications.
Big Data has been characterized by what experts refer to as the 3 Vs:
- the large volume of data in many environments;
- the wide variety of data types frequently stored in big data systems; and
- the velocity at which much of the data is generated, collected and processed.
The Big Data revolution we’ve seen over the past few years has brought substantial technological advancements in data storage, cloud computing and data science, which helps businesses identify patterns and trends. This growing discipline is also becoming one that companies need to understand, embrace, socialize and build in their overall culture to continue to be successful in a quickly evolving commerce industry.
Outstanding opportunities exist today for companies willing to embrace the Big Data revolution and leverage the power of data insights. Some of the latest technological innovations across the industry, especially in artificial intelligence, would not be possible if we didn’t have access to large amounts of data sets, in real-time, and to large data cloud storage solutions.
Coupled with the great computational powers we see in machines, Big Data has opened opportunities to develop exceptional algorithms and reach immense progress in machine learning and deep learning.
This makes Big Data one of the fundamental commerce pillars for companies who want to succeed in delivering optimized online experiences that better respond to shoppers’ needs.
Big Data ecommerce specifically refers to the use of big data analytics and technologies to improve customer engagement, online personalization, and sales’ growth. It offers flexibility, scalability, richness of features and can provide businesses with insights into shopper behaviors to generate fully personalized experiences across every digital touch point that were not previously possible.
Specifically Big Data ecommerce has opened opportunities in:
- Personalization: Big Data allows companies to leverage machine learning to derive targeted insights on their shoppers’ behaviors and consequently deliver personalized experiences and suggestions based on individual preferences; historical behavior; needs’ predictions. Big Data allows for refined customers’ segmentation that can be leveraged to offer customized loyalty incentives and promotions. In fact 86% of consumers say that personalization plays an important role in their buying decisions.
- SEO optimization: Big Data can provide brands and retailers valuable insights into what shoppers are searching for, allowing them to fully optimize and refresh product detail pages, ensuring products appear at the top of search results.
- Customer Service: Big Data can be leveraged to manage customer service, allowing brands and retailers to understand what customers are looking for, what they need, and how satisfied they are with a product or a brand. Big Data can also be used to analyze customer satisfaction surveys and queries to further improve products and quality.
- CRM: Big Data makes it easier for online companies to identify what features or products are most important to different types of shoppers, prioritizing feature developments and innovations accordingly, and building stronger relationships with shoppers.
- Marketing automation: Big Data can be leveraged to design machine learning systems that deliver more targeted, engaging, and personalized marketing communications and campaigns to online shoppers. Machine learning can lead to new trends’ and customer segment’s identification, allowing to deliver more efficient and targeted marketing campaigns that will improve brands’ ROI.
Some companies already put to the test these opportunities with L’Oréal employing data scientists to analyze the effects of various cosmetic agents on different skin textures; Rolls Royce has been leveraging Big Data to analyze data from airplane engines for maintenance scheduling; Feedzai has been regularly using AI to analyze data to detect fraud.
Leveraging the full potential of Big Data would not be possible without the art of Data Science to fully understand, and maximize the potential of insights that can be generated from large data sets using the right technology.
Data science expertise has historically been challenging for companies to fulfill. Hiring specialists, experienced in-demand data scientists wasn’t easy. However, with the availability of new tools and systems fueled by AI, as well as organizational cultural shifts, data science is becoming more and more embedded across organizations as a whole.
Long gone are the times when data analysis and data science were isolated, elitist pockets of knowledge.
The systems and technologies that are now available in the market to engineers, developers, and analysts, allow organizations to do more with less. Data scientists and analysts have the opportunity to now rely on high-performing and complex machine learning and AI technologies to solve more complex problems with less expertise. Inevitably, this has led to the rise of data science democratization, making it an embedded cultural discipline for companies willing to maintain their competitive advantage online.
However, as companies have more and more access to data, ethical, privacy, and compliance implications need to be taken into account and carefully understood. Transparency with online shoppers around data collection and usage will be essential for companies willing to succeed and build long-term relationships with their customers, fostering loyalty and increasing lifetime value.
Managing Big Data and data scientists will require experienced leadership, strong ethical considerations, and product knowledge, making it more important for companies to build these competencies internally, rather than relying on outsourced services.
Responsible senior leadership and management teams will need to accurately understand the implications of sourcing ‘clean’ data to create AI models free of biases, free of unlawful information, and free of illegal and unreliable sources.
Most businesses were fully unprepared for the enormous supply chain disruptions caused by the global pandemic and retailers were hit very hard. Online players have had to rethink their supply chain models, leveraging their omnichannel capabilities to improve fulfillment options and inventory flows between physical and online shopping channels (refer to the Omnichannel Focus below on this post).
As logistics and transportation costs went through the roof and as sustainability became paramount for the businesses of today and tomorrow, more efficient supply chain models and delivery capabilities have emerged. Coupled with a growing omnichannel approach for retailers globally, this has opened new opportunities for supply chain models and management to reduce delivery touchpoints and warehousing costs.
Shopify research identified key trends for brands to master their supply chain and last mile capabilities, continuing to win in ecommerce and omnichannel retail. Below are some of the most interesting 2023 trends:
● Last Mile optimization
The Last Mile is the most critical portion and most expensive component of the fulfillment process, accounting for 50% of the total cost of shipping. It also represents the most important step, being the final delivery touchpoint to the end customer.
With sustained ecommerce growth globally, last mile logistics will continue to be an important aspect in the future. The ecommerce sector requires seamless processes and quick deliveries to meet customer needs, but there are some challenges along the way that have been reinforced by the growth of third-party logistics companies; unpredictable fuel costs; and labor costs.
Grocery and retail brands are responding to these costs’ increases by taking ownership of the last mile. According to Maggie M. Barnett, COO of Ship Hero, omnichannel retailers are curtailing the impact of global supply chain disruptions via “micro-fulfillment,” handling fulfillment directly with supplies from a local warehouse. Retailers then continue to invest in buy online, deliver from store and buy online, pick up in-store.
For example, In 2021, Target employed micro-fulfillment strategies like adding local distribution centers. This helped fuel a 45% increase in drive-up pick-up orders in 2021, prompting the company to add 18,000 parking spaces for pick-ups nationwide.
● Elevating supply chain executives to the C level
Last year, Modern Retail called the role of supply chain specialist “the hottest job in retail.”
After the significant disruptions caused to supply chains globally after the pandemic, C-level executives realized the need to invest in senior executive leaders solely focused on supply chain and fulfillment operations.
For example, Carmel Hagen, the founder of baking brand Supernatural, hired a head of operations to facilitate its new relationships with Amazon and Whole Foods, staging that “Technically, the right time to make the operations hire was probably three to six months before I got there….But I knew for sure it was time.”
● Increasing inventory reserves
Ensuring inventory buffers and increasing reserves is like planning for rainy days and we all know too well the famous fable of the grasshopper and the ant…
According to McKinsey’s How COVID 19 is reshaping supply chains’ study , 47% of companies across a variety of industries planned to increase inventory supplies during the pandemic in 2020. Within the past 12 months, the number of companies planning on doing the same has increased to 60%.
However, decisions to do so are not straightforward as they carry significant implications on sourcing inventory and increasing available volumes, opening the door to regional sourcing networks, rather than over-relying on global ones.
Regionalization remains a key priority for companies and almost 90% of respondents from the study said that they expect to pursue some degree of regionalization during the next three years, while 100 % of respondents from the healthcare and engineering, construction, and infrastructure sectors said the approach was relevant to their sector.
● Investing in supply chain agility
Improving and optimizing the supply chain often requires internal business transformations and a greater focus on business agility to be able to face adversities and uncertainties, quickly adapting to change.
Surveys suggest improvements in companies’ “decisions making” speed at a rate of five to 10 times when focusing on agility. Those without the agility focus improved by only two times.
Some senior leaders understand the connection between agility and a responsive supply chain, as in the case of Henkel’s laundry and home care business, where chief supply chain officer Dirk Holback says agility investments paid off during the pandemic:
[Henkel has] invested in setting up the right organization, rebuilt our footprint, implemented digital, and developed sustainability capabilities. … [I]n April of last year, when the first demand shocks hit our system, we introduced a new element in our S&OP [sales and operations planning] process in just a few days—basically a daily management of capacity and demand by country supported by some digital capabilities using our existing analytics platform.
● Investing in the customer experience
Supply chain management may not sound as glamorous as marketing management, but it is essential to customer experience and satisfaction. How frustrating can it be to wait too long for your online deliveries? To have to pay for late deliveries? To not be able to contact someone in customer service to locate your shipment?
We’ve all been there and needless to say these issues will make or break an experience with a particular brand or retailer, leaving unhappy customers behind. Forrester already predicts brands will lose 50% of sales on back-ordered products. The remedy to that is companies that can provide a customer experience satisfying enough to make up for late deliveries.
Lenovo already invested in stronger customer service capabilities, increasing the breadth of their customers’ insights: from customer surveys, to customer sentiment on social media. Leveraging this additional data allowed Lenovo to uncover major root causes for late deliveries and address them to improve the rate of on-time deliveries by 6%.
● Improving supply chain forecasting
Forecasting global economic trends is a challenge without perfect answers. According to McKinsey, 32% of businesses blamed bad forecasting for the issues faced in the supply chain during the global pandemic.
To improve forecasting, companies had to think creatively and find new ways to leverage data and insights using tech innovation like artificial intelligence to better predict demand, and inventory flows across locations. With new delivery models emerging in ecommerce, the integration of systems to monitor inventory, shipments and consumer behavior is essential to improve forecasting capabilities in an environment where physical stores also become pick up delivery points.
The fundamental questions to address for optimized forecasting now need to cover all the below:
-
- What is the lifespan of the products? Are they perishable or can they remain on shelves in a warehouse indefinitely?
- How often are the products sold?
- How are sales affected by different seasons, months, and special sales events?
- What are the warehouse fees associated with a particular item?
- By what date do you need to reorder inventory for each product?
- What are your standard reorder points?
- Do you require safety stock?
● Investing in technology and analytics
Access to data, data usability and data science can all contribute to improved supply chain management. We’ve long heard about the benefits of leveraging data to improve conversion and return on investment for marketing activities, but it can also drive powerful effects on the supply chain, adding more flexibility and agility.
Predictive analytics, fueled by advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, coupled with innovation in robotics’ process automations will have profound impact on retailers and manufacturers. Allowing for better forecasting, waste reductions, optimized fulfillment, these new solutions will not only contribute positively to supply chain management, but will also deliver an important impact on carbon footprint and CO2 emissions’ reductions.
- Investing in Sustainability
More and more consumers are concerned about the environmental impact of items they purchase. According to Simon Kucher, 75% of global consumers feel that environmental sustainability is as important or more to them now than it was last year. Additionally, 66% of consumers rank sustainability as one of the top five drivers behind a purchase decision, up from 50% last year. Companies can have a real impact on carbon footprint reduction by optimizing their fulfillment routes; leveraging AI technologies to optimize inventory warehousing; using electric vehicles for deliveries; and rethinking their packaging solutions to prefer recyclable and reusable materials.
- Prioritizing speedier deliveries
Consumers are demanding more from their suppliers: a recent study by Mckinsey in the US revealed that 90% of consumers expect shipments to be delivered within two to three days and around 46% abandon their shopping cart if the estimated delivery time is too long.
Consumers have gotten used to exceptional delivery options over the last few years for ecommerce purchases. With Amazon Prime; Prime Now; same-day deliveries; online consumers now start their shopping journey with incredibly high expectations and this is something that companies cannot ignore.
- Drones and delivery robots
New technologies have fueled a myriad of new delivery options that are being tested for speed and greater efficiency. Drones and delivery robots are two key technology innovations that answer some of the needs retailers are facing today.
Delivery drones are aerial devices that can deliver packages to customers. They can deliver packages quickly and efficiently, especially in areas that are difficult for traditional delivery vehicles to reach. Delivery robots are small autonomous robots that can deliver packages to customers in urban settings.
Both solutions are relying on similar technologies that are powering self-driving cars and both have benefitted from the exceptional advancement in AI we’ve witnessed over the past few years.
This type of last mile delivery is responding to very important needs that have emerged such as contactless deliveries, super speedy deliveries, and more fuel efficient solutions.
The world of commerce is evolving fast and the logistics and supply chain sector is actively working to keep up. Leveraging technology innovation, and gaining a front seat at companies’ leadership teams, supply chain functions are becoming essential to the success of online retailers and brands willing to succeed in ecommerce.
I previously published a brief post dedicated to Social Commerce, a channel that offers significant opportunities for brands willing to win online.
(https://jdelmar.com/2020/02/16/the-social-commerce-opportunity/)
Social Commerce is expected to grow at a CAGR of 31% through to 2030, and approximately half of Gen Z and Millennials already purchase products on social media channels. Specifically, social media channels have played an important role in the product discovery phase of the shopping journey, with approximately 30% of online shoppers leveraging them for new product discoveries.
Social commerce allows businesses to connect with their customers directly and personally, providing a new way of engaging with potential buyers on social media platforms like Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, Snap, and TikTok. With the help of mobile technology, businesses can engage with their customers in real-time, launching campaigns and promotions that are tailored to specific target audiences.
Social commerce also allows brands to create highly personalized experiences for each customer based on their interests and preferences, while providing insights into customer behavior that can be used to improve customer service and product offerings.
We already see a variety of highly successful social commerce strategies, including:
- Influencers’ Marketing: leveraging influencers and their important followers’ audiences to increase reach and generate affinity with potential shoppers.
- Brands’ partnerships: partnering with established brands to drive product awareness and generate new leads.
- Exclusive offers: trial new product launches and drive engagement through exclusive and personalized product offerings.
- Exclusive loyalty programs and promotions: drive engagement and conversion through personalized, limited-time offers only accessible via these channels.
- Entertainment, Gamification & Virtual experiences: delivering fun, gamified shoppable experiences that mix tech innovations, like AR and VR, with social reach and shareable events.
Overall, businesses can take advantage of social media platforms to reach large numbers of potential customers quickly, while also increasing brand awareness within minutes.
TikTok, in particular, has become one of the fastest growing social commerce opportunities, and in 2023 brands and retailers should define their own TikTok strategy to capitalize on this space.
Companies like Meta and Snap have dominated the social commerce scene in previous years and while they are more established, TikTok has quickly stolen the spotlight with a growing community of over 1B users globally.
TikTok has been one of the driving forces behind video contents contributing to the growth of Video and Live commerce in the social commerce realm. Forging their leadership position in the space, ByteDance, TikTok’s parent company, acquired Musical.ly in 2017.
Meta quickly followed by heavily investing in their video content capabilities launching several video content options for Instagram ranging from Reels, to Live, to Stories, and Instagram Video.
Despite Facebook and Instagram having larger shopping bases than TikTok, the audiences on TikTok are more engaged and according to recent surveys from Bazaarvoice, people who shop on TikTok browse and buy goods more frequently than shoppers on other social media channels.
For online retailers and brands, especially those selling direct-to-consumer, TikTok is opening massive opportunities to target engaged audiences with a high propensity to buy. Single videos can go a long way, driving viral effects, high engagement and conversion.
75% of TikTok users say that content on the platform inspires them to buy, even when they are not actively on a shopping mission. This was clearly illustrated with the popularity of the #TikTokMadeMeBuyIt hashtag which generated over 7.4B views in 2021.
Video commerce or Livestream commerce has also been growing in popularity over the years, gaining significant traction in markets like China, subsequently expanding in Western cultures through social media networks. (https://jdelmar.com/2021/11/07/the-booming-of-live-commerce/ ).
With a tech-savvy and mobile-first market of 1B internet users, China has led the way globally in the digital commerce market for years. Live streaming Ecommerce has consequently been a very popular way for brands to sell on marketplaces online, leveraging the power of influencers. With very strong momentum during Singles Day mega deal events in China, livestreams hosted by reputable influencers have been attracting several millions customers. Influencer Viya, for example, attracted more than 43 million customers during Taobao’s Singles Day event in 2019, confirming the power of live shopping and influencer marketing.
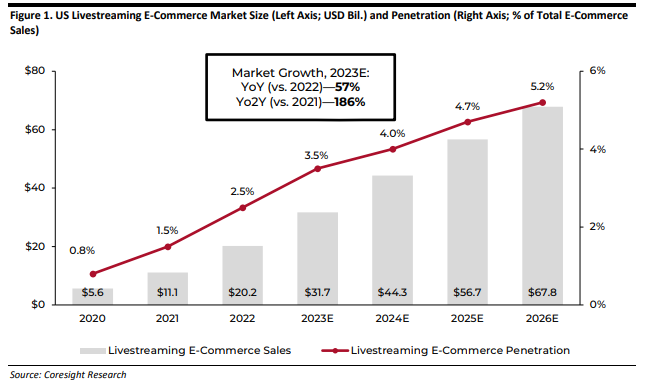
Livestream commerce will continue to connect retailers to shoppers through 2023, creating new opportunities for companies across the retail space. The livestream ecommerce market is highly popular with Gen-Z and it is expected to grow to $32B, with a total expected share of ecommerce of more than 5% by 2026 in the US.
McKinsey has already predicted that live commerce could well account for 10 to 20% of all ecommerce sales globally by 2026, making it an attractive channel for brands to leverage.
As retail companies are increasingly rethinking the role of shoppable livestreams in their overall business strategy, they will use emerging retail tech and a variety of live streaming formats to meet consumer demand and deliver personalized experiences.
Live commerce has opened up new value propositions for brands and retailers selling online. Customers can enjoy an immersive shopping experience from the comfort of their homes, view products in detail, and ask questions before making a purchase. Additionally, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior and tailor their offerings to meet customer needs.
Fueled by technological advancements, livestream shopping will become more feature-rich, with retailers offering customers the opportunity to explore products using AR / VR technology, and potentially experience live shopping sessions within virtual environments like the Metaverse. This will allow customers to interact with products as if they were in a physical store, making informed purchase decisions.
By relying on digital solutions like video shopping platforms, businesses can lower their overhead costs, improving the overall shopping experience, while still providing quality service and support from knowledgeable sales associates through chatbots or live chat features.
Key trends are emerging for brands willing to succeed with Live Commerce in 2023:
- Utilize Emerging Technology
US consumers use on average 2.5 platforms daily and on top of social media channels, brands and retailers now have the opportunity to host livestream shopping events on their own platforms to strengthen shopper loyalty, drive engagement and collect 1st-party data.
User data empower sales and ecommerce teams to spend time engaging with targeted customers and craft the right assortment, advice and personalized customer communications. Live streaming can also support personalization and although the one-to-many live stream shopping format remains the most prominent, Coresight Research expects consultation type live shopping events to grow in popularity as more companies adopt hyper-targeted and personalized channels’ strategies.
- Promote Live streaming Programs
Livestream adopters have found that the pace of communication is as important as the quality of interactions and the information shared with viewers. Regular live streams are essential to growing a loyal customer base over time and expert marketers maintain regular live streaming schedules to establish daily, weekly, monthly events depending on the target audience and preferred live streaming format.
Incentives, in the form of discounts and giveaways, are also standard practices in livestreaming shopping events that can attract new audiences by creating a sense of urgency and clear call to actions. In fact, according to Coresight Research, participating in product giveaways is the top ranked reason cited by 36% of online shoppers as the main reason for watching a livestream event.
- Transform content to what consumers desire
Live stream shopping will expand into new shopping verticals and it is already being adopted across a variety of retail sectors. The home improvement and grocery sectors have been the latest investors in the space, suggesting the opportunity to leverage these new formats for daily and routine occasions.
Additionally, educational content is also gaining popularity as B2B companies already report success with content focused on product education, product use cases, and usage incentives.
Companies need to focus on what live stream viewers want: discovering new products; getting product information; and learning from experts in the field to be inspired.
Finally, transparency from retail companies will become a critical factor requested by online consumers. From sustainability in manufacturing, to inclusivity in staffing, to societal impact, brands will be able to showcase their commitments through live streams in an engaging and transparent way. This will in turn generate positive trust from consumers and added sales.
- Partner with Talent to expand online communities
Authentic conversations will continue to drive organic viewer growth. Social media influencers and celebrities are effective livestream hosts as they boost viewership by leveraging established follower bases. Peer reviews and industry experts can share product and brand expertise, which is more and more appreciated by consumers seeking transparency and authenticity.
Customers with authentic testimonials are particularly popular with Gen X with 44% ranking real-life customers as their most-preferred type of livestream hosts.
Company live streams are also key media to build and strengthen communities. In addition to building and maintaining a strong presence on social media networks, companies can also cultivate online communities and drive traffic and conversion through livestreams on their owned websites and apps.
Traditional media is about mass impressions and awareness. Retail Digital Media, or RDM, is digital advertising that supports brand commercial activities to drive sales at a specific eRetailer.
According to statistics, ecommerce product purchases will likely account for 95% of overall purchases by 2040. This ratio provides a great understanding of the online buyer potential and how frequently internet users engage in ecommerce shopping. As consumers spend more and more time researching products online, it becomes paramount for brands and sellers to reach individual shoppers and get closer to the point of purchase at the right time.
As eRetailers launch their own media solutions and partner with global top tier agencies, such as Carrefour with Publicis, brands have to invest in and understand the new tools available to reach their consumers along the shopping funnel.
From brand building, to brand awareness, to driving conversions, strategies are available in ways that become more efficient thanks to AI technologies and Big Data. eRetailers have quickly grasped the opportunities generated by growing amounts of online traffic and shoppers ‘in market’ to cleverly monetize the need for brands to surface in online search results and across digital touch points.
Retail Media has opened the opportunity to target online shoppers at every stage of the online shopping funnel. Today, 75% of shoppers online research products on eRetailers instead of traditional search engines like Google and eRetailers understand the increasing competition amongst brands who want to capture a larger share of voice on their virtual infinite shelves.
This phenomenon has pushed eRetailers to substantially invest in developing advertising tools that allow brands to differentiate themselves from their competition by targeting relevant ‘in-market’ consumers’ audiences. New suites of advertising products with sophisticated data-driven targeting functionalities are now available on major eRetailers like Amazon, Walmart, Carrefour, Instacart,...
From brand building, to brand awareness, to driving conversions, strategies are available in ways that become more efficient thanks to AI technologies and Big Data.
eRetailers have now realized retail digital media is and will continue to be a fundamental part of their revenue streams.
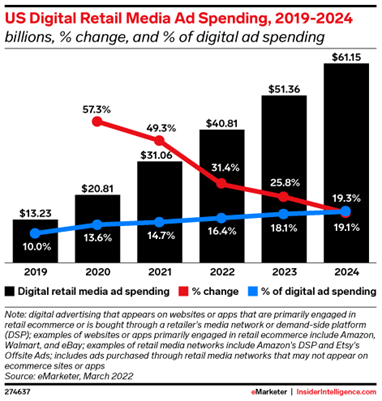
In the US alone, $44B were spent on retail digital media in 2022, and $51B are expected to be spent this year with a further $61B in 2024.
Brands will need to modify their advertising budgets and justify the shifts towards retail digital media, involving a broader range of stakeholders. Sales, finance, brand, and marketing teams will need to design new investment strategies to fully leverage the opportunities raised by retail digital media. In fact, according to Statista, still only 2.2% of visits to ecommerce stores result in conversions, making retail digital media a very attractive proposition to interact with potential buyers.
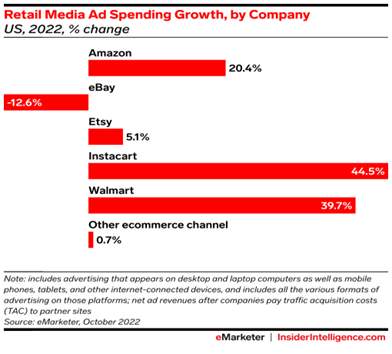
eMarketer's 2022 report stated that companies such as Amazon, Walmart, Instacart, eBay and Home Depot already announced that they are expanding their Retail Media Networks.
Recent research from McKinsey also revealed that 75% of non-CPG advertisers plan to increase their spending in retail media.
A survey conducted by Merkle on retailers, brands, and CPGs around retail media highlights that:
- 81% of CPGs intend to increase their media budgets with Retail Media.
- 62% of CPGs seek to collaborate with retail media networks for access to their first-party data.
- 58% of CPGs anticipate a closer relationship with the retailer via Retail Media.
Thanks to the reach and targeting possibilities offered by retail digital media, brands can separate target client segments and choose the campaign elements that are most appropriate for each group, maximizing their ROI and chances to convert.
As a result of this increased level of personalization, companies also benefit from access to a retailer's first-party customer data to target customers based on their unique requirements and develop relationships with them.
In fact, Retail Media Ads, as opposed to other forms of media, give advertisers the benefit of directly tying their advertising budget to real conversions, and other customers’ actions, making it incredibly attractive from a revenue management perspective.
Can we still speak of individual retail channels? Certainly not. Being omnichannel is what makes brands successful in today’s commerce industry and what will allow them to win in the future of commerce.
Physical stores made a quick comeback after the global pandemic, but they too are undergoing a revolution. A revolution which is driving more and more interconnectivity. Online to offline, offline to online, store to mobile device, to social media platform, to D2C website, to online marketplace....
Today’s retail experience is fully interconnected, allowing for better engagement, personalization, and convenience.
It is more and more important for brands to meet their customers wherever they are along the shopping journey, being present with the right message at the right time. Addressing the needs of consumers at every stage of the purchasing funnel is what will distinguish successful brands from laggers.
Researching online, purchasing in store and vice versa (ROPO); buying online picking up in store (BOPIS); comparing availability across digital and physical shelves; expecting seamless personalized customer service across every shopping destination are just some of the mainstream expectations from today’s shoppers.
Being multichannel means businesses must be able to sell to and communicate with customers through multiple channels at any given moment. This may look like having a website; a Facebook shop; and an Instagram account. Omnichannel is the next level up, and it’s the future of ecommerce. Currently, 52% of ecommerce sites already have omnichannel capabilities.
Building omnichannel capabilities into an ecommerce site requires an intimate understanding of the consumers’ audiences. Creating a seamless experience is what will retain a customer, driving repeat purchases. In fact, companies that have robust omnichannel strategies retain almost 89% of their customers, whereas companies with weak omnichannel strategies have a 33% customer retention rate. Key retailers and brands who have strongly invested in omnichannel capabilities, are seeing highly successful results.
Target continued to drive investments towards their BOPIS capabilities, loading online orders in customers’ cars in under 2 hours. Disney delivered a highly personalized Disney Experience app to allow their theme parks’ visitors to customize their visits according to personal interests. Walgreens further enhanced their digital experience, allowing customers to reorder prescriptions online by scanning barcodes on their medications, easily picking them up in stores.
Strong omnichannel strategies do more than enhance the experience of online shoppers. According to McKinsey, the more channels a sales company has, the more market shares a company gains.
Quoting Victoria Morrissey from Ferguson Enterprises: ‘The power of true omnichannel is understanding all the channels our customers use, and how they want to use them, throughout their entire journey. If you don’t understand what that journey is, you can’t provide the right information at the right time’.
Concluding Thoughts
With an expected revenue of $6.3 T in 2023, ecommerce is growing, and here to stay. Brands and retailers who want to win in this space will need to embrace change as a ‘constant’ of their modus operandi.
Consumers are tech savvy, hyper-connected, mission-driven and they demand more and more from brands online. Being at the right place, at the right time, with the right message and consistent brand values is non-negotiable to win in this game.
Despite the macro-economic global crises we’ve been facing during the pandemic, and following the Russian-Ukraine conflict, the dramatic advancements in technology innovation are fueling incredible opportunities in an omnichannel commerce world.
Artificial intelligence (AI) allows eRetailers and brands to optimize their operational processes with significant impact on supply chain management and logistics. It also opens key opportunities for online experience optimization; personalization; social listening; and customer service innovation.
Brands and retailers that will take the time to understand these new technologies and embed them within their business strategies, will emerge with a strong competitive advantage.
The rise of Web 3.0, coupled with innovations in AI and new virtual experiences is already tangible. Brands and retailers are experimenting with the Metaverse; with digital wallets; NFTs; blockchain technologies to create engaging and delightful avenues to shop online. With an expected market impact of $2T by 2030, ecommerce will be the largest value contributor to the Metaverse, where new communities of shoppers will be able to bond with the brands they love and where the boundaries between shopping channels will disappear. Commerce will find its way into virtual showrooms; gaming platforms; and virtual shopping events.
The rise and importance of social and live commerce are already building the path towards new shopping experiences that mix entertainment with gamification and platforms like TikTok are unveiling new exciting opportunities for brands to reach audiences in exciting and impactful ways.
Change and adaptability are a must for brands and eRetailers looking to win in ecommerce in 2023 and beyond, and key trends can already be adopted to succeed: Technology Innovation; Supply Chain and Last Mile Delivery Management; Social & Live Commerce; Retail Digital Media Networks; Fostering an Omnichannel Approach.
Bambuser, 2023. 10 Key Trends Shaping Livestreaming E-Commerce in 2023. Available at : https://9302266.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/9302266/Innovator%20Report/10-Key-Trends-Shaping-Livestreaming-E-Commerce-in-2023-Feb-1-2023.pdf?utm_medium=email&_hsmi=244091372&_hsenc=p2ANqtz-8QLM6dQTrVEasBR21FTLzZV8QQzYm-qgb0mfs6puQgShfDfnlM7nzN1OO8EVP7LwJZr472Z4Us1pIjBFhC_hnmt9S3-VYM9-ZEbaC-J1CkBAj6XAc&utm_content=244091372&utm_source=hs_automation
Bringg, 2021. Last Mile Delivery: New Rules for the eCommerce Era. Available at : https://www.bringg.com/resources/guides/last-mile-delivery/
Commercetools, 2022. 2022 Gartner Magic Quadrant™ and Critical Capabilities for Digital Commerce .Available at :https://commercetools.com/resources/analyst-report/gartner-magic-quadrant?utm_source=Paid%20Search&utm_medium=Google%20Search&utm_content=Gartner-Report-2022&utm_campaign=Analyst%20Report%20Gartner&utm_term=ecommerce&utm_campaign=Analyst%20Report%20Gartner%20BPK%20Hub-Leads%20DACH&utm_source=adwords&utm_medium=ppc&hsa_acc=1309061964&hsa_cam=19733925079&hsa_grp=154861620948&hsa_ad=649181655793&hsa_src=g&hsa_tgt=kwd-10160771&hsa_kw=ecommerce&hsa_mt=b&hsa_net=adwords&hsa_ver=3&gclid=Cj0KCQiAgaGgBhC8ARIsAAAyLfEP1_MtvXKH5K2nKW15T2K8e0kuMS6uO1JgZS7gEB3QWHhBJW-ppLUaAiFOEALw_wcB
Ecommerce Germany, 2023. What you need to know about last mile in e-commerce. Available at :https://ecommercegermany.com/blog/what-you-need-to-know-about-last-mile-in-e-commerce#:~:text=Last%20mile%20logistics%20is%20a,sent%20directly%20to%20the%20customer.
Esw, 2022. THE GROWING ROLE OF AR AND VR IN ECOMMERCE . Available at : https://esw.com/blog/the-growing-role-of-ar-and-vr-in-ecommerce/
FarEye, 2022. Last-mile e-commerce significance and challenges in delivery operations. Available at :https://fareye.com/resources/blogs/last-mile-ecommerce
Forbes, 2023. A Wild Ride: 6 Takeaways From The Ever-Changing World Of Commerce. Available at: https://www-forbes-com.cdn.ampproject.org/c/s/www.forbes.com/sites/jonbird1/2023/03/07/a-wild-ride-ahead-6-takeaways-from-the-ever-changing-world-of-commerce/amp/
GoWit Technology, 2022. Why Retail Media Is Essential For E-commerce Companies and Brands? Available at :https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/why-retail-media-essential-e-commerce-companies-brands-gowit-adtech/
IBM, 2023. Build smarter supply chains with AI and blockchain. Available at :https://www.ibm.com/supply-chain?utm_content=SRCWW&p1=Search&p4=43700075222129322&p5=p&gclid=Cj0KCQjwmN2iBhCrARIsAG_G2i7JO2OMxAtbQecwGrYVRtxNCYreqlLnAeuTFZ4F-MS7Eti80WACCmAaAhw1EALw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds
Infotech, 2021. 5 ways Amazon and Alibaba use AI and data mining to increase e-commerce sales. Available at: https://infotech.report/articles/5-ways-amazon-and-alibaba-use-ai-and-data-mining-to-increase-e-commerce-sales
Intel, 2023. Demystifying the Virtual Reality Landscape. Available at : https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/tech-tips-and-tricks/virtual-reality-vs-augmented-reality.html
Intelistyle, 2023. Fashion AI In 2023: What is Trending This Year. Available at: https://www.intelistyle.com/fashion-ai-in-2023-what-should-we-expect-to-see-this-year/#:~:text=From%20business%20operations%20to%20e,AI%20in%20their%20business%20models.
Master of Code, 2023. Artificial intelligence (AI) in eCommerce: Statistics & Facts, Use Cases, and Benefits. Available at :https://masterofcode.com/blog/state-of-artificial-intelligence-ai-in-ecommerce-statistics-and-deployment
McKinsey, 2022. Value creation in the metaverse. Available at : https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/business%20functions/marketing%20and%20sales/our%20insights/value%20creation%20in%20the%20metaverse/Value-creation-in-the-metaverse.pdf
McKinsey, 2023. The new B2B growth equation. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/the-new-b2b-growth-equation
Paack, 2023. Last Mile Trends to Know About in 2023. Available at :https://paack.co/last-mile-trends-to-know-about-in-2023/
Sas, 2023. Future of retail. Available at : https://www.sas.com/en/whitepapers/future-of-retail-113037.html?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=non-cbo-gbc-edn-emea&gclid=Cj0KCQiAgaGgBhC8ARIsAAAyLfEWwIlOm3f872Ivf8XrN91S_gIyOEXBsXfeVg2dFtdlAEw-Yk8ni3caAt6aEALw_wcB
Shopify, 2022. How Augmented Reality (AR) is Changing Ecommerce Shopping. Available at: https://www.shopify.com/enterprise/augmented-reality-ecommerce-shopping
Shopify, 2022. Supply Chain Trends That Will Shape 2023. Available at :https://www.shopify.com/enterprise/supply-chain-trends-strategies
Statista, 2023. AR & VR – Worldwide. Available at : https://www.statista.com/outlook/amo/ar-vr/worldwide
Statista, 2023. E-commerce as percentage of total retail sales worldwide from 2015 to 2026. Available at :https://www.statista.com/statistics/534123/e-commerce-share-of-retail-sales-worldwide/#:~:text=In%202021%2C%20e%2Dcommerce%20accounted,percent%20of%20retail%20sales%20worldwide.